Osmosis | osmotic pressure | types of solution on the basis of osmotic pressure | isotonic solution | hypotonic solution | hypertonic solution | reverse osmosis |
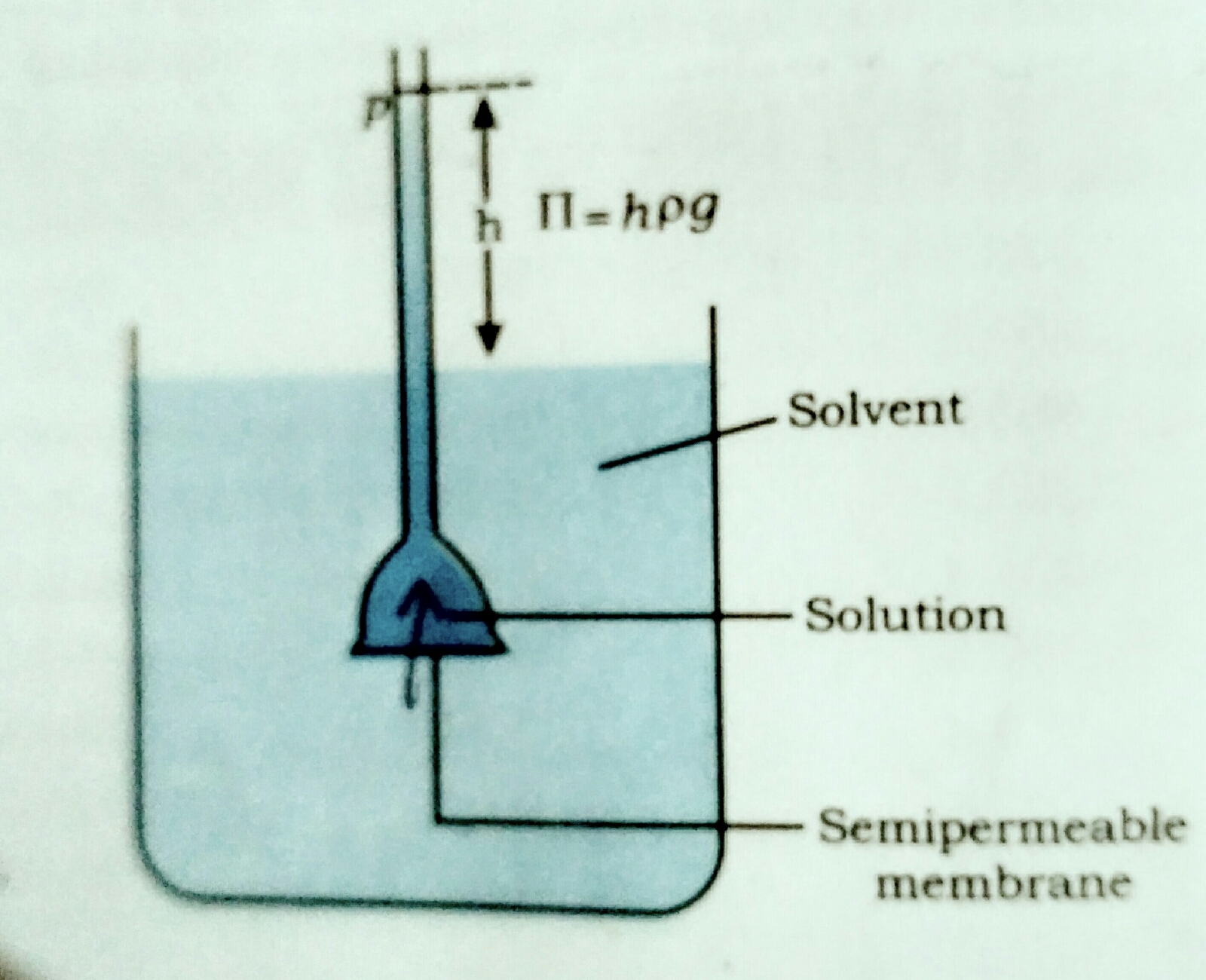
Osmosis : ✓ Spontaneous uni-directional movement of solvent through semi permeable membrane from lower concentration of solution to higher concentration of solution is known as osmosis. [ Here Lower concentration of solution means a Diluted solution ( in which amount of solute is less than the amount of solvent. ) And higher concentration of solution means a concentrated solution ( in which amount of solute is more than amount of solvent .) Semipermeable membrane (SPM) : membrane having a network of submicroscopic holes or pores by which small molecule like solvent can pass through it but larger molecule like salute is hindered is known as semi permeable membrane. ] Osmotic pressure (π) : ✓ The extra pressure applied on the side of solution so that the net flow of solvent through the semipermeable membrane is stoped , the extra pressure is known as osmotic pressure. ✓ Osmotic pressure represent as pi (π). By experiment it is found that os...