Osmosis | osmotic pressure | types of solution on the basis of osmotic pressure | isotonic solution | hypotonic solution | hypertonic solution | reverse osmosis |
Osmosis :
✓ Spontaneous uni-directional movement of solvent through semi permeable membrane from lower concentration of solution to higher concentration of solution is known as osmosis.
[ Here Lower concentration of solution means a Diluted solution ( in which amount of solute is less than the amount of solvent. )
And higher concentration of solution means a concentrated solution ( in which amount of solute is more than amount of solvent .)
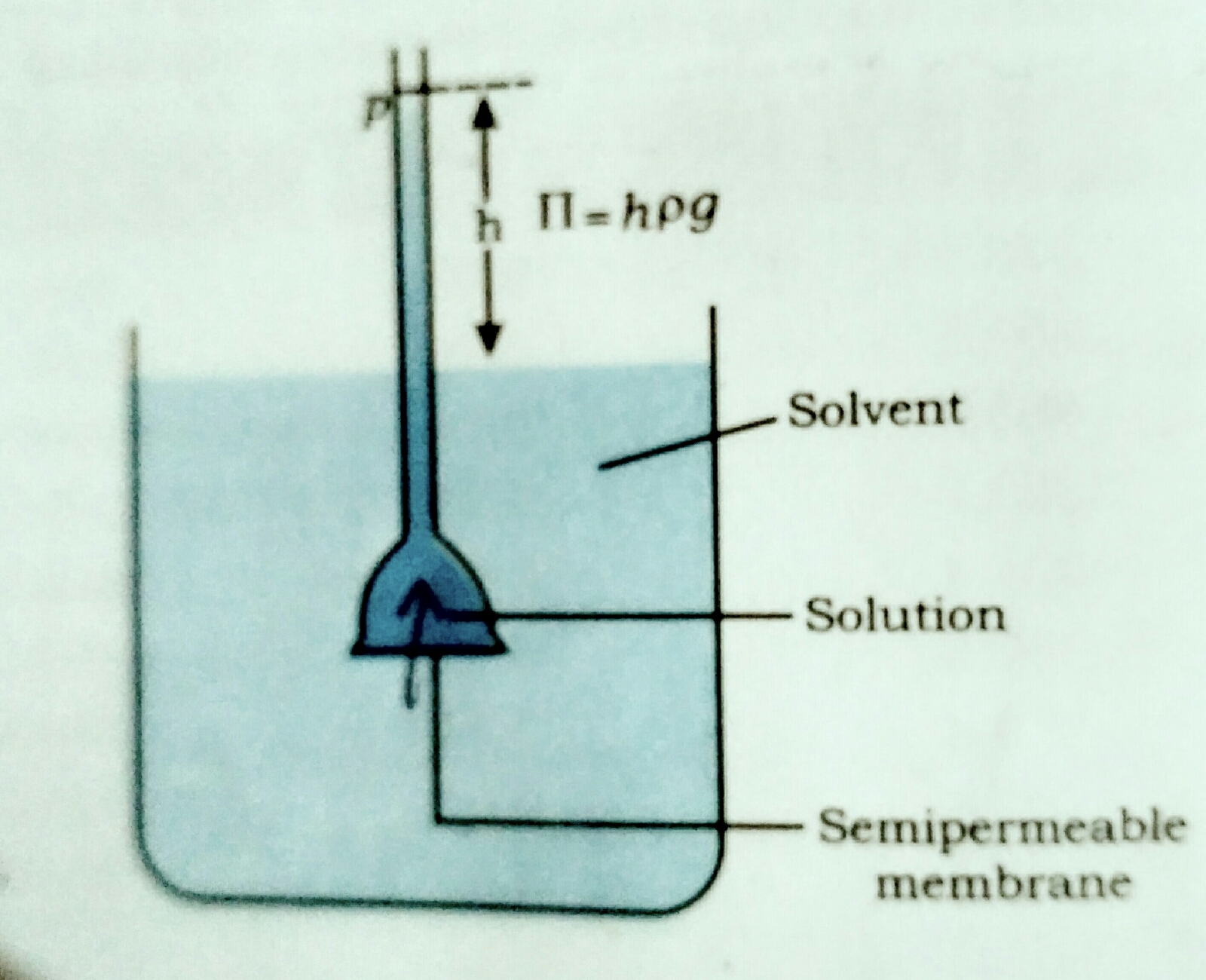
Semipermeable membrane (SPM) :
membrane having a network of submicroscopic holes or pores by which small molecule like solvent can pass through it but larger molecule like salute is hindered is known as semi permeable membrane. ]
Osmotic pressure (π) :
✓ The extra pressure applied on the side of solution so that the net flow of solvent through the semipermeable membrane is stoped , the extra pressure is known as osmotic pressure.
✓ Osmotic pressure represent as pi (π).
By experiment it is found that osmotic pressure is directly proportional to Molarity of the solution and also temperature.
So ,
π = RMT
[ Here R is solution constant and value of R is 0.082 atm - litter/ mole- Kelvin
M is molarity of the solution
T is temperature in Kelvin ]
✓ On the basis of osmotic pressure solution are of three types --
1. Isotonic solution
2. Hypotonic solution
3. Hypertonic solution
1. Isotonic solution :
At a given temperature if two solution having same osmotic pressure then the solution is known as isotonic solution.
examples: 0.02 M urea solution age isotonic with 0.02 M glucose solution.
2. Hypotonic solution :
At a given temperature If a solution having lower osmotic pressure than other one solution then the solution is known as hypotonic solution.
examples; 0.04 M urea is hypertonic to 1M (molar) of glucose solution.
3. Hypertonic solution :
At a given temperature if a solution having higher osmotic pressure than the other one solution , then the solution is known as hypertonic solution.
examples ; 1M ( one molar ) sucrose solution is hypertonic with 0.05 molar urea solution.
Reverse osmosis (R.O.) :
✓ Non-spontaneous process in which direction of osmosis is reversed when applied pressure is larger than osmotic pressure , then this type of phenomenon is known as reverse osmosis.
✓ reverse osmosis is used for purification of water.

Comments
Post a Comment